Present Value: Definition, & Calculation
Content
- Present value formula for different annuity types
- Step 3. Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Exercise Assumptions
- Practical tips to getting paid faster and avoid missing on wide array of avenues, including credit, cash, check, or bitcoin.
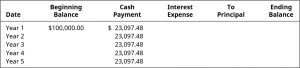
- Example: Calculating Monthly Mortgage payments
- How to Calculate the Future Value of an Investment
- What is the Time Value of Money?
Starting off, the cash flow in Year 1 is $1,000, and the growth rate assumptions are shown below, along with the forecasted amounts. We’ll assume a discount rate of 12.0%, a time frame of 2 years, and a compounding frequency of one. In short, a more rapid rate of interest compounding results in a lower present value for any future payment. Net present value is the difference between the present value of cash inflows and the present value of cash outflows over a period of time. Present value is the concept that states an amount of money today is worth more than that same amount in the future. In other words, money received in the future is not worth as much as an equal amount received today.

This illustrates how important the period is or “Nper” is in excel, bearing in mind this is a period input as opposed to a date input. When using the FV calculation, investors may forecast the amount of profit that different types of investment opportunities can earn with differing degrees of accuracy.
Present value formula for different annuity types
We obtain $620.92, the present value of $1000 in 5 years with a How To Calculate Present Value Of A Future Amount of return of 10% annually. The formula can also be used to calculate the present value of money to be received in the future.
It is the value in today’s dollars of a https://personal-accounting.org/ in the future. One of the most important reasons to use present value is to account for inflation and loss in purchasing power. When calculating future value, we are starting with money today, which is most valuable because money today can be invested at the same guaranteed risk-free rate. The future value of that money is the amount we can expect to have from this baseline activity of depositing it in the bank at the guaranteed risk-free interest rate r.
Step 3. Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Exercise Assumptions
Usually, the time period is 1 year, which is why it is called an annuity, but the time period can be shorter, or even longer. In this particular example, the present value amount is relatively small. The difference between the two functions will be more significant when a more substantial sum is present valued. Regardless of this fact, from an auditor’s perspective, they will not raise an audit difference based on the present value function selected. An annuity is a constant amount of money received in each period, usually for an outlay of money today. Consider an annuity that pays W dollars every period for n periods starting k periods from now.
